|
matplotlib pyplots_Examples 26_pyplot_scales. |
H.Kamifuji . |
- pyplot_scales.py
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from matplotlib.ticker import NullFormatter # useful for `logit` scale # Fixing random state for reproducibility np.random.seed(19680801) # make up some data in the interval ]0, 1[ y = np.random.normal(loc=0.5, scale=0.4, size=1000) y = y[(y > 0) & (y < 1)] y.sort() x = np.arange(len(y)) # plot with various axes scales plt.figure(1) # linear plt.subplot(221) plt.plot(x, y) plt.yscale('linear') plt.title('linear') plt.grid(True) # log plt.subplot(222) plt.plot(x, y) plt.yscale('log') plt.title('log') plt.grid(True) # symmetric log plt.subplot(223) plt.plot(x, y - y.mean()) plt.yscale('symlog', linthreshy=0.01) plt.title('symlog') plt.grid(True) # logit plt.subplot(224) plt.plot(x, y) plt.yscale('logit') plt.title('logit') plt.grid(True) # Format the minor tick labels of the y-axis into empty strings with # `NullFormatter`, to avoid cumbering the axis with too many labels. plt.gca().yaxis.set_minor_formatter(NullFormatter()) # Adjust the subplot layout, because the logit one may take more space # than usual, due to y-tick labels like "1 - 10^{-3}" plt.subplots_adjust(top=0.92, bottom=0.08, left=0.10, right=0.95, hspace=0.25, wspace=0.35) plt.show()
- 実行結果( pyplot_scales.png )
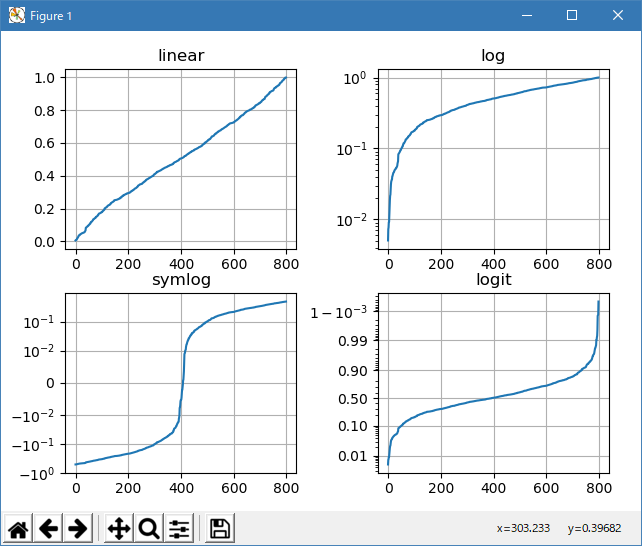
Python 3.11.2 見直しました。上記のコードでは、下記のエラーが発生します。
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "_:\pyplot_scales.py", line 37, in <module>
plt.yscale('symlog', linthreshy=0.01)
File "C:\Users\_____\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python311\Lib\site-packages\matplotlib\pyplot.py", line 3113, in yscale
return gca().set_yscale(value, **kwargs)
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
File "C:\Users\_____\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python311\Lib\site-packages\matplotlib\axes\_base.py", line 74, in wrapper
return get_method(self)(*args, **kwargs)
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
File "C:\Users\_____\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python311\Lib\site-packages\matplotlib\axis.py", line 810, in _set_axes_scale
ax._axis_map[name]._set_scale(value, **kwargs)
File "C:\Users\_____\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python311\Lib\site-packages\matplotlib\axis.py", line 767, in _set_scale
self._scale = mscale.scale_factory(value, self, **kwargs)
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
File "C:\Users\_____\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python311\Lib\site-packages\matplotlib\scale.py", line 714, in scale_factory
return scale_cls(axis, **kwargs)
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
TypeError: SymmetricalLogScale.__init__() got an unexpected keyword argument 'linthreshy'
matplotlib 内部のエラーのようです。matplotlib の改修(先祖帰りバグの改修)を待つしかない。
Python 3.11.6 (matplotlib 3.7.1) では、下記のようなエラーがあり、実行できない。
Traceback (most recent call last): File "M:\______\pyplot_scales.py", line 37, in
Python 3.12.9 (matplotlib 3.8.1) では、下記のようなエラーがあり、実行できない。plt.yscale('symlog', linthreshy=0.01) File "C:\Users\______\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python311\Lib \site-packages\matplotlib\pyplot.py", line 3113, in yscale return gca().set_yscale(value, **kwargs) ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ File "C:\Users\______\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python311\Lib \site-packages\matplotlib\axes\_base.py", line 74, in wrapper return get_method(self)(*args, **kwargs) ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ File "C:\Users\______\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python311\Lib \site-packages\matplotlib\axis.py", line 810, in _set_axes_scale ax._axis_map[name]._set_scale(value, **kwargs) File "C:\Users\______\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python311\Lib \site-packages\matplotlib\axis.py", line 767, in _set_scale self._scale = mscale.scale_factory(value, self, **kwargs) ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ File "C:\Users\______\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python311\Lib \site-packages\matplotlib\scale.py", line 714, in scale_factory return scale_cls(axis, **kwargs) ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ TypeError: SymmetricalLogScale.__init__() got an unexpected keyword argument 'linthreshy'
Traceback (most recent call last): File "E:\______\pyplot_scales.py", line 37, in
Python 3.11.6 (matplotlib 3.7.1) 及び Python 3.12.0 (matplotlib 3.8.1) で、見直し中、新しいサンプル( scales-scales-py ) を見つけ、下記のコードで、正常に実行できました。plt.yscale('symlog', linthreshy=0.01) File "C:\Program Files\Python312\Lib\site-packages\matplotlib\pyplot.py", line 4167, in yscale gca().set_yscale(value, **kwargs) File "C:\Program Files\Python312\Lib\site-packages\matplotlib\axes\_base.py", line 73, in wrapper return get_method(self)(*args, **kwargs) ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ File "C:\Program Files\Python312\Lib\site-packages\matplotlib\axis.py", line 837, in _set_axes_scale ax._axis_map[name]._set_scale(value, **kwargs) File "C:\Program Files\Python312\Lib\site-packages\matplotlib\axis.py", line 796, in _set_scale self._scale = mscale.scale_factory(value, self, **kwargs) ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ File "C:\Program Files\Python312\Lib\site-packages\matplotlib\scale.py", line 717, in scale_factory return scale_cls(axis, **kwargs) ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ TypeError: SymmetricalLogScale.__init__() got an unexpected keyword argument 'linthreshy'
""" ====== Scales ====== Illustrate the scale transformations applied to axes, e.g. log, symlog, logit. The last two examples are examples of using the ``'function'`` scale by supplying forward and inverse functions for the scale transformation. """ import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np from matplotlib.ticker import FixedLocator, NullFormatter # Fixing random state for reproducibility np.random.seed(19680801) # make up some data in the interval ]0, 1[ y = np.random.normal(loc=0.5, scale=0.4, size=1000) y = y[(y > 0) & (y < 1)] y.sort() x = np.arange(len(y)) # plot with various axes scales fig, axs = plt.subplots(3, 2, figsize=(6, 8), layout='constrained') # linear ax = axs[0, 0] ax.plot(x, y) ax.set_yscale('linear') ax.set_title('linear') ax.grid(True) # log ax = axs[0, 1] ax.plot(x, y) ax.set_yscale('log') ax.set_title('log') ax.grid(True) # symmetric log ax = axs[1, 1] ax.plot(x, y - y.mean()) ax.set_yscale('symlog', linthresh=0.02) ax.set_title('symlog') ax.grid(True) # logit ax = axs[1, 0] ax.plot(x, y) ax.set_yscale('logit') ax.set_title('logit') ax.grid(True) # Function x**(1/2) def forward(x): return x**(1/2) def inverse(x): return x**2 ax = axs[2, 0] ax.plot(x, y) ax.set_yscale('function', functions=(forward, inverse)) ax.set_title('function: $x^{1/2}$') ax.grid(True) ax.yaxis.set_major_locator(FixedLocator(np.arange(0, 1, 0.2)**2)) ax.yaxis.set_major_locator(FixedLocator(np.arange(0, 1, 0.2))) # Function Mercator transform def forward(a): a = np.deg2rad(a) return np.rad2deg(np.log(np.abs(np.tan(a) + 1.0 / np.cos(a)))) def inverse(a): a = np.deg2rad(a) return np.rad2deg(np.arctan(np.sinh(a))) ax = axs[2, 1] t = np.arange(0, 170.0, 0.1) s = t / 2. ax.plot(t, s, '-', lw=2) ax.set_yscale('function', functions=(forward, inverse)) ax.set_title('function: Mercator') ax.grid(True) ax.set_xlim([0, 180]) ax.yaxis.set_minor_formatter(NullFormatter()) ax.yaxis.set_major_locator(FixedLocator(np.arange(0, 90, 10))) plt.show() # %% # # .. admonition:: References # # The use of the following functions, methods, classes and modules is shown # in this example: # # - `matplotlib.axes.Axes.set_xscale` # - `matplotlib.axes.Axes.set_yscale` # - `matplotlib.axis.Axis.set_major_locator` # - `matplotlib.scale.LinearScale` # - `matplotlib.scale.LogScale` # - `matplotlib.scale.SymmetricalLogScale` # - `matplotlib.scale.LogitScale` # - `matplotlib.scale.FuncScale`
- 参照ページ
pyplots_Examples code: pyplot_scales.py
scales-scales-py
- リリースノート
- 2023/12/08 Ver=1.04 Python 3.12.0 (matplotlib 3.8.1)で確認
- 2023/12/08 Ver=1.04 Python 3.11.6 (matplotlib 3.7.1)で確認
- 2023/04/04 Ver=1.03 Python 3.11.2 で確認
- 2020/11/02 Ver=1.01 Python 3.7.8 で確認
- 2018/12/06 Ver=1.01 初版リリース
- 関連ページ