|
pylab_examples_Examples 50_customize_rc. |
H.Kamifuji . |
- customize_rc.py
私はここでよく見えるようにしようとはしていませんが、その場でrcパラメータをカスタマイズするいくつかの例を示すだけです
インタラクティブに作業したい場合や、Figure のために異なるデフォルトセットを作成する必要がある場合(たとえば、パブリッシュのデフォルトのセットを 1 つ、インタラクティブな探査のセットの 1 つ)、デフォルトを設定するカスタムモジュールにいくつかの関数を定義し、 例えば、
""" I'm not trying to make a good looking figure here, but just to show some examples of customizing rc params on the fly If you like to work interactively, and need to create different sets of defaults for figures (e.g., one set of defaults for publication, one set for interactive exploration), you may want to define some functions in a custom module that set the defaults, e.g., def set_pub(): rc('font', weight='bold') # bold fonts are easier to see rc('tick', labelsize=15) # tick labels bigger rc('lines', lw=1, color='k') # thicker black lines (no budget for color!) rc('grid', c='0.5', ls='-', lw=0.5) # solid gray grid lines rc('savefig', dpi=300) # higher res outputs Then as you are working interactively, you just need to do >>> set_pub() >>> subplot(111) >>> plot([1,2,3]) >>> savefig('myfig') >>> rcdefaults() # restore the defaults """ import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.subplot(311) plt.plot([1, 2, 3]) # the axes attributes need to be set before the call to subplot plt.rc('font', weight='bold') plt.rc('xtick.major', size=5, pad=7) plt.rc('xtick', labelsize=15) # using aliases for color, linestyle and linewidth; gray, solid, thick plt.rc('grid', c='0.5', ls='-', lw=5) plt.rc('lines', lw=2, color='g') plt.subplot(312) plt.plot([1, 2, 3]) plt.grid(True) plt.rcdefaults() plt.subplot(313) plt.plot([1, 2, 3]) plt.grid(True) plt.show()
- 実行結果( customize_rc.png )
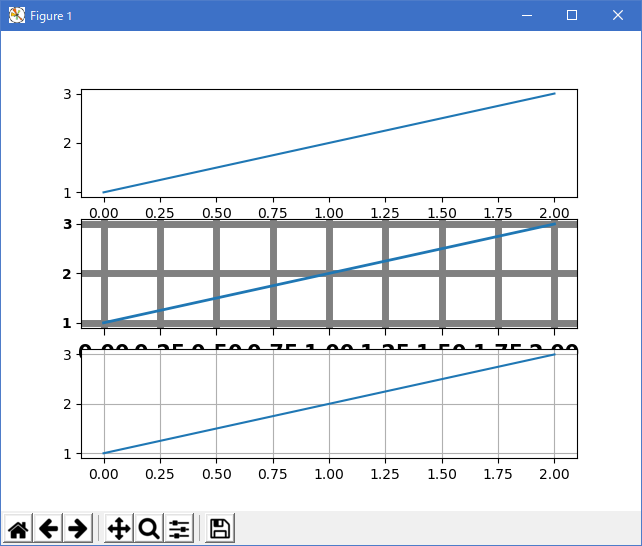
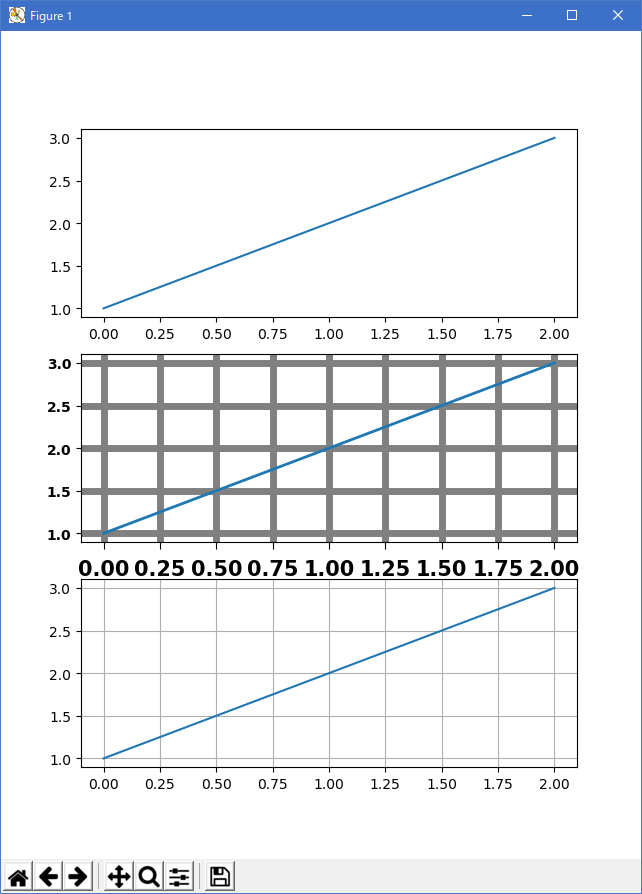
- 参照ページ
pylab_examples_Examples code: customize_rc.py
- リリースノート
- 2023/04/01 Ver=1.03 Python 3.11.2 で確認
- 2020/10/31 Ver=1.01 Python 3.7.8 で確認
- 2018/11/28 Ver=1.01 初版リリース
- 関連ページ